FAQ
Frequently asked questions on decarbonization
How does decarbonization work?
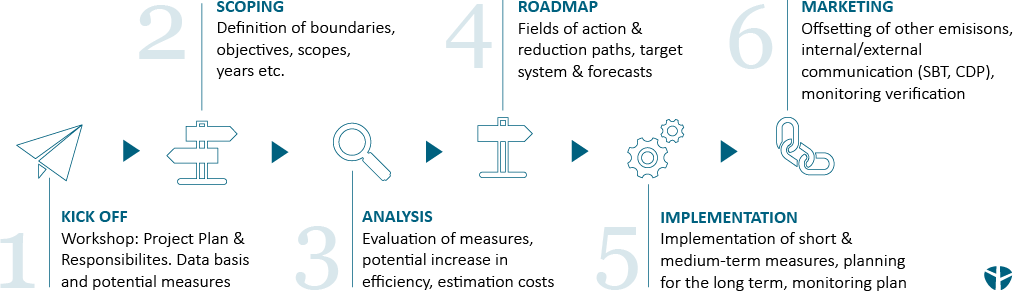
Decarbonization works according to a clear procedure. The first step is to calculate the carbon footprint at the company or product level for Scope 1,2 and 3. To decarbonize, climate targets are then set within the company and mitigation measures are planned to reduce the carbon footprint. For Scope 1&2, low-carbon power generation becomes more important and the use of fossil fuels is reduced accordingly. Energy efficiency assessments and a shift to renewable energy sources also take place. For Scope 3, mitigation measures are more complex, as suppliers, partners, and customers need to be engaged, to implement measures to reduce this footprint. A typical hotspot can be found within Scope 3.1 – Purchased Goods and Services.
What are the main co-benefits of decarbonization?
Companies that manage to reduce their upstream and downstream emissions (Scope 1 2 3 emissions) gain competitive advantages due to energy saving, the early switch to renewable energy sources and customized solutions in order to strengthen their business. Moreover, they shape the green transition and contribute towards achieving the goals of the EU Green Deal. Human emissions of CO2 and other greenhouse gases (GHG) are the primary causes of climate change. Sustainable development depends on climate action. Therefore, climate action (SDG 13) is one of the Sustainable Development Goals of the UN 2030 agenda.
Which measures are effective for decarbonization?
Decarbonization efforts should follow a strict hierarchy:
- Avoid energy consumption
- Reduce energy consumption by increasing efficiency
- Cover remaining energy consumption with renewable energy sources
- Neutralize the unavoidable emissions
How does decarbonization lead to lower risks?
Climate change leads to multiple risks across all countries, sectors and industries. The IPCC report continuously provides evidence of the massive impact of global warming. Therefore, climate risk is already considered a financial risk. Decarbonization or climate strategies help to mitigate the risks, as companies can not only contribute to climate change mitigation but also prepare for or avoid risks. Learn now how TCFD can help you gain a better understanding of your risks related to climate change.
Why is a decarbonization strategy important for the future?
National legislation imposes strict obligations on companies to mitigate climate change and meet the Paris Agreement goals. In order to limit global warming to between 1.5 degrees Celsius and 2 degrees Celsius, the requirements and carbon tax costs will increase massively in the coming years. However, decarbonization measures affect all corporate divisions and the entire value chain. Due to the complexity of decarbonization and climate strategies, there is no time to lose.